#t-sql - data types
Explore tagged Tumblr posts
Text
Top 5 Selling Odoo Modules.
In the dynamic world of business, having the right tools can make all the difference. For Odoo users, certain modules stand out for their ability to enhance data management and operations. To optimize your Odoo implementation and leverage its full potential.
That's where Odoo ERP can be a life savior for your business. This comprehensive solution integrates various functions into one centralized platform, tailor-made for the digital economy.
Let’s drive into 5 top selling module that can revolutionize your Odoo experience:
Dashboard Ninja with AI, Odoo Power BI connector, Looker studio connector, Google sheets connector, and Odoo data model.
1. Dashboard Ninja with AI:
Using this module, Create amazing reports with the powerful and smart Odoo Dashboard ninja app for Odoo. See your business from a 360-degree angle with an interactive, and beautiful dashboard.
Some Key Features:
Real-time streaming Dashboard
Advanced data filter
Create charts from Excel and CSV file
Fluid and flexible layout
Download Dashboards items
This module gives you AI suggestions for improving your operational efficiencies.
2. Odoo Power BI Connector:
This module provides a direct connection between Odoo and Power BI Desktop, a Powerful data visualization tool.
Some Key features:
Secure token-based connection.
Proper schema and data type handling.
Fetch custom tables from Odoo.
Real-time data updates.
With Power BI, you can make informed decisions based on real-time data analysis and visualization.
3. Odoo Data Model:
The Odoo Data Model is the backbone of the entire system. It defines how your data is stored, structured, and related within the application.
Key Features:
Relations & fields: Developers can easily find relations ( one-to-many, many-to-many and many-to-one) and defining fields (columns) between data tables.
Object Relational mapping: Odoo ORM allows developers to define models (classes) that map to database tables.
The module allows you to use SQL query extensions and download data in Excel Sheets.
4. Google Sheet Connector:
This connector bridges the gap between Odoo and Google Sheets.
Some Key features:
Real-time data synchronization and transfer between Odoo and Spreadsheet.
One-time setup, No need to wrestle with API’s.
Transfer multiple tables swiftly.
Helped your team’s workflow by making Odoo data accessible in a sheet format.
5. Odoo Looker Studio Connector:
Looker studio connector by Techfinna easily integrates Odoo data with Looker, a powerful data analytics and visualization platform.
Some Key Features:
Directly integrate Odoo data to Looker Studio with just a few clicks.
The connector automatically retrieves and maps Odoo table schemas in their native data types.
Manual and scheduled data refresh.
Execute custom SQL queries for selective data fetching.
The Module helped you build detailed reports, and provide deeper business intelligence.
These Modules will improve analytics, customization, and reporting. Module setup can significantly enhance your operational efficiency. Let’s embrace these modules and take your Odoo experience to the next level.
Need Help?
I hope you find the blog helpful. Please share your feedback and suggestions.
For flawless Odoo Connectors, implementation, and services contact us at
[email protected] Or www.techneith.com
#odoo#powerbi#connector#looker#studio#google#microsoft#techfinna#ksolves#odooerp#developer#web developers#integration#odooimplementation#crm#odoointegration#odooconnector
4 notes
·
View notes
Text
Software & Tools Training: Unlock Your Digital Potential with Gritty Tech
In a technology-driven world, proficiency in digital tools is no longer optional—it’s essential. Whether you're an entrepreneur, freelancer, or working professional, upgrading your skills through structured Software & Tools Training can be the most impactful decision for your career. At Gritty Tech, we believe learning should be practical, accessible, and results-oriented For More...
We provide high-quality education focused on real-world application. Our Software & Tools Training programs are designed to meet the diverse needs of individuals and businesses across industries. With a network of professional tutors spanning over 110 countries, we’ve created a global community committed to continuous learning.
What Is Software & Tools Training?
Software & Tools Training refers to structured learning programs that help individuals understand and effectively use digital software and applications. This includes training in productivity software like Microsoft Office, cloud-based platforms like Google Workspace, data analysis tools such as Excel and Tableau, project management systems like Jira and Trello, and specialized applications like Adobe Photoshop, AutoCAD, or QuickBooks.
These programs are not just about clicking buttons—they’re about understanding functionality, improving workflows, and mastering practical problem-solving using digital solutions.
Why Choose Software & Tools Training?
Career Advancement Employees with advanced digital skills stand out in job markets. Many job roles now require knowledge of multiple software tools. Our training ensures you're fully equipped.
Efficiency and Productivity Learning to use tools efficiently leads to faster task execution, fewer mistakes, and better team collaboration.
Business Growth For businesses, trained staff leads to optimized operations, better data handling, and smarter decision-making.
Remote Work Readiness In an increasingly remote-first world, understanding collaboration and project tools is critical. Our Software & Tools Training includes guidance on tools like Slack, Zoom, and Asana.
Why Gritty Tech is the Right Choice
Gritty Tech has positioned itself as a trusted name in online learning, especially for professionals seeking Software & Tools Training. Here’s what sets us apart:
1. Global Network of Tutors
We have a network of tutors in over 110 countries. Each trainer is not only certified but also experienced in practical applications of the tools they teach. This ensures our learners receive relevant, up-to-date, and hands-on instruction.
2. Affordable Pricing
We’re committed to providing top-tier education at rates that make sense. Our Software & Tools Training programs are priced competitively, making them accessible without compromising on quality.
3. Flexible Payment Plans
We offer flexible payment options, including monthly and session-wise plans. Whether you’re an individual learner or a corporate client, we tailor solutions to fit your budget.
4. Easy Refund and Tutor Replacement Policy
Satisfaction is key. If you're not happy with a session or tutor, we provide easy refunds or replacement tutors to ensure you always receive quality education.
5. Customized Learning Paths
Our courses are not one-size-fits-all. We assess your goals and design personalized training plans to help you learn at your pace and preference.
Types of Software & Tools Training Offered
Office Productivity Tools
Microsoft Excel, Word, PowerPoint
Google Docs, Sheets, Slides
Design & Creative Software
Adobe Photoshop, Illustrator, Premiere Pro
Canva for business
Accounting and Finance Tools
QuickBooks, Zoho Books
Microsoft Dynamics
Data Analysis Tools
Excel Advanced, Power BI, Tableau
SQL basics for data handling
Project Management Software
Jira, Trello, Monday.com
Asana and ClickUp
Collaboration & Communication
Slack, Zoom, Microsoft Teams
Notion and Evernote
We also offer custom corporate Software & Tools Training tailored to industry needs.
How Software & Tools Training Aligns with Industry Demands
Recruiters and HR professionals consistently list software proficiency as a top requirement. Companies rely on digital tools to track projects, communicate across teams, manage customer data, and analyze performance.
With technologies evolving rapidly, the ability to learn and adapt to new software is considered a critical skill. Gritty Tech’s training helps individuals bridge this gap efficiently.
What to Expect from Our Training Sessions
Interactive live sessions with certified tutors
Practical, task-oriented exercises
Access to recordings and downloadable resources
Assessment-based progress tracking
Certificates upon course completion
Every session is structured to deliver value—combining theory with applicable knowledge you can use immediately.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is Software & Tools Training?
Software & Tools Training is a guided learning program focused on teaching individuals and teams how to effectively use digital applications for productivity, collaboration, design, and analysis.
2. Who can benefit from Software & Tools Training?
Anyone—from students to CEOs—can benefit from Software & Tools Training. Whether you’re learning to use Excel for data or Photoshop for design, we have a course for you.
3. Is Software & Tools Training at Gritty Tech beginner-friendly?
Yes, our Software & Tools Training programs start with foundational topics and gradually move to advanced applications, making them ideal for beginners and experienced users alike.
4. How long does Software & Tools Training take?
Training duration depends on the tool and your learning pace. We offer short-term crash courses and longer, in-depth programs depending on your requirements.
5. Do I receive a certificate after completing the Software & Tools Training?
Yes. After completing your Software & Tools Training, you receive a verified certificate, which can be added to your resume or LinkedIn profile.
6. Are there live classes or only recorded sessions?
We offer both. You can attend live, interactive classes or access recorded sessions at your convenience as part of your Software & Tools Training plan.
7. Can I switch tutors during my Software & Tools Training?
Absolutely. If you're not satisfied, Gritty Tech provides easy tutor replacement options to ensure the best learning experience throughout your Software & Tools Training journey.
8. Do you offer Software & Tools Training for teams and companies?
Yes. We provide enterprise-level Software & Tools Training tailored for businesses, including employee upskilling programs and group sessions.
9. How is Gritty Tech’s Software & Tools Training different from others?
We offer hands-on, practical training led by global tutors, with flexible payment plans, personalized support, and a satisfaction guarantee.
10. How do I enroll in Software & Tools Training with Gritty Tech?
Enrollment is easy. Visit our official website, choose your desired course under Software & Tools Training, select your plan, and get started in minutes.
Conclusion
Software is the language of modern business. Without the ability to use digital tools, professionals risk falling behind in a fast-paced world. That’s why investing in Software & Tools Training is not just beneficial—it’s essential.
Gritty Tech has reimagined how software skills are taught by creating a system that is efficient, affordable, and learner-focused. With our commitment to quality education, global tutor support, and flexible learning paths, you can confidently upgrade your skillset and open new career opportunities.
Let your learning journey begin with Gritty Tech. Explore our Software & Tools Training programs today and take the first step toward digital mastery.
Would you like me to generate the SEO Title and Meta Description for this content now?
0 notes
Text
Top Data Analysis Methods in 2025: A Complete Guide for Beginners and Professionals

🚀 Introduction: Why Data Analysis Methods Matter Today
We live in a world overflowing with data—from social media stats and website clicks to sales transactions and customer feedback. But raw data alone is meaningless. It’s only through the use of data analysis methods that we can extract actionable insights and make informed decisions.
Whether you’re a business owner, student, analyst, or entrepreneur, understanding data analysis methods is no longer optional—it’s essential.
In this article, we’ll explore the most widely used data analysis methods, their benefits, tools, use cases, expert opinions, and FAQs—all written in a human-friendly, easy-to-understand tone.
🔍 What Are Data Analysis Methods?
Data analysis methods are systematic approaches used to examine, transform, and interpret data to discover patterns, trends, and insights. These methods range from simple descriptive statistics to complex predictive algorithms.
By using the right method, businesses and analysts can:
📈 Identify trends
💡 Solve business problems
🔮 Forecast future outcomes
🎯 Improve performance
📘 Types of Data Analysis Methods
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the major types of data analysis methods you should know in 2025:
1. Descriptive Analysis
Goal: Summarize historical data to understand what has happened. Example: Monthly revenue report, user growth trends.
Techniques Used:
Mean, median, mode
Frequency distribution
Data visualization (charts, graphs)
Best Tools: Excel, Tableau, Google Data Studio
2. Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA)
Goal: Explore the dataset to uncover initial patterns, detect outliers, and identify relationships. Example: Discovering patterns in customer purchase history.
Techniques Used:
Box plots, scatter plots, heat maps
Correlation matrix
Data cleaning
Best Tools: Python (Pandas, Matplotlib), R, Power BI
3. Inferential Analysis
Goal: Make predictions or generalizations about a larger population based on sample data. Example: Predicting election results based on sample polling.
Techniques Used:
Hypothesis testing
Confidence intervals
T-tests, chi-square tests
Best Tools: SPSS, R, Python (SciPy)
4. Diagnostic Analysis
Goal: Determine the causes of a past event or outcome. Example: Why did the bounce rate increase last month?
Techniques Used:
Root cause analysis
Regression analysis
Data mining
Best Tools: SQL, Power BI, SAS
5. Predictive Analysis
Goal: Forecast future outcomes based on historical data. Example: Predicting next month’s sales based on seasonal trends.
Techniques Used:
Machine learning (decision trees, random forest)
Time series analysis
Neural networks
Best Tools: Python (Scikit-learn, TensorFlow), IBM Watson
6. Prescriptive Analysis
Goal: Recommend actions based on predicted outcomes. Example: Suggesting product pricing for maximum profitability.
Techniques Used:
Optimization
Simulation modeling
Decision trees
Best Tools: MATLAB, Excel Solver, Gurobi
7. Quantitative Analysis
Goal: Focus on numerical data to understand trends and measure outcomes. Example: Measuring website conversion rates.
Techniques Used:
Statistical modeling
Data aggregation
Regression
8. Qualitative Analysis
Goal: Analyze non-numerical data like text, images, or videos. Example: Analyzing customer reviews or survey responses.
Techniques Used:
Sentiment analysis
Thematic coding
Content analysis
Best Tools: NVivo, Lexalytics, Google NLP API
💼 Use Cases of Data Analysis Methods in the Real World
Here’s how businesses use these methods across industries:
🛍 Retail
Method Used: Predictive & diagnostic
Purpose: Forecast demand, understand sales dips
💳 Banking
Method Used: Inferential & prescriptive
Purpose: Detect fraud, assess risk
🏥 Healthcare
Method Used: Diagnostic & descriptive
Purpose: Patient outcome analysis, treatment optimization
📱 Tech Companies
Method Used: Exploratory & predictive
Purpose: App usage patterns, churn prediction
🛠 Best Tools for Applying Data Analysis Methods
Tool NameKey FeaturesSuitable ForExcelCharts, pivot tables, formulasBeginnersPythonML, EDA, statistical analysisIntermediate to ExpertR LanguageStatistical modeling, data visualizationIntermediateTableauVisual dashboardsBusiness analystsPower BIIntegration with Microsoft appsEnterprisesSQLQuerying large datasetsData engineers
🌟 Real Reviews From Experts
“I started with Excel for simple descriptive analysis and gradually moved to Python for predictive modeling. The transition was smoother than I expected.” – Neha D., Data Analyst at a Startup
“We used prescriptive methods in Power BI to optimize our logistics routes. Saved us 20% in transport costs within three months.” – Arjun K., Supply Chain Manager
“Using EDA methods helped us detect user drop-off points in our app, which we quickly fixed.” – Priya S., UX Designer
📌 Step-by-Step Guide to Choosing the Right Data Analysis Method
Define Your Objective: What do you want to find out?
Identify Data Type: Is it qualitative or quantitative?
Choose Your Tool: Based on your team’s skill level.
Clean the Data: Remove duplicates, null values, outliers.
Apply the Method: Use the appropriate model/technique.
Visualize & Interpret: Create charts to simplify interpretation.
Take Action: Use insights to make data-driven decisions.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
🔹 Q1. What is the difference between data analysis methods and data analysis techniques?
A: Methods refer to the broad approach (e.g., descriptive, predictive), while techniques are specific tools or processes (e.g., regression, clustering).
🔹 Q2. Which data analysis method should I use as a beginner?
A: Start with descriptive and exploratory analysis. These are easy to learn and highly insightful.
🔹 Q3. Do I need coding skills to use these methods?
A: Not always. Tools like Excel, Tableau, and Power BI require minimal to no coding. For advanced analysis (e.g., machine learning), coding helps.
🔹 Q4. Can I use multiple methods in one project?
A: Absolutely! Many real-world projects use a combination of methods for deeper insights.
🔹 Q5. Which is the most powerful data analysis method?
A: That depends on your goal. For forecasting, predictive analysis is powerful. For decision-making, prescriptive analysis works best.
🧠 Tips to Master Data Analysis Methods in 2025
📝 Take online courses (Coursera, Udemy, DataCamp)
💻 Practice with real datasets (Kaggle, Google Dataset Search)
🧮 Understand the math behind techniques
📊 Visualize findings to communicate better
👥 Collaborate with other analysts and teams
✅ Conclusion: Your Data, Your Power
Data is no longer just for analysts or IT professionals. In 2025, knowing how to use data analysis methods can set you apart in virtually any profession. From optimizing marketing campaigns to launching new products, these methods empower you to make data-driven decisions with confidence.
So whether you’re just starting out or looking to level up, keep experimenting, keep analyzing, and let your data tell the story.
🌐 Read more expert data analysis content at diglip7.com 📩 Have questions? Drop a comment or connect with us for consultation.
0 notes
Text
Exploring the Various Types of Triggers in T-SQL Server
Exploring the Various Types of Triggers in T-SQL Server Hello, T-SQL enthusiasts! In this blog post, I will introduce you to Types of Triggers in T-SQL Server – one of the most powerful and essential features in T-SQL Server. Triggers are special procedures that automatically execute in response to specific events on a table or view. They play a crucial role in maintaining data integrity,…
0 notes
Text
Transitioning from Data Analyst to Data Scientist: A Roadmap to Success
In today's data-driven world, businesses rely heavily on data to make informed decisions. While data analysts play a crucial role in interpreting and visualizing data, data scientists go a step further by building predictive models and extracting deeper insights using machine learning. If you are a data analyst looking to transition into a data scientist role, this blog will guide you through the essential steps, required skills, and the best training programs to help you achieve your career goal.
Understanding the Difference: Data Analyst vs. Data Scientist
Before looking into the transition process, it's important to understand the key differences between the two roles:
Data Analysts primarily work with structured data, using tools like Python, SQL, Excel, and visualization platforms (Power BI, Tableau). Their main focus is on reporting, trend analysis, and business intelligence.
Data Scientists go beyond reporting by applying statistical modeling, machine learning, and artificial intelligence to predict outcomes and optimize business strategies. They work with large datasets and use programming languages like Python and R for advanced analytics.
If you are currently a data analyst, making the leap to data science requires upskilling in areas such as machine learning, statistics, and programming. Here’s a structured roadmap to help you make a smooth transition.
1. Strengthen Your Programming Skills
Data analysts often rely on SQL and Excel, but data scientists need proficiency in programming languages like Python and R. These languages are widely used for data manipulation, statistical analysis, and machine learning.
Learn Python: Python is the most popular language for data science due to its simplicity and powerful libraries (Pandas, NumPy, Scikit-learn, TensorFlow).
Master R: R is widely used in academia and research for statistical computing and data visualization.
Enhance your SQL skills: Strong SQL skills are necessary for data extraction and handling large databases.
2. Gain Expertise in Statistics and Mathematics
A strong foundation in statistics and mathematics is essential for data scientists. Unlike data analysts, who primarily focus on descriptive statistics, data scientists need to understand inferential statistics, probability theory, and linear algebra.
Study Probability and Statistics: Concepts like hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and distributions are fundamental in machine learning.
Learn Linear Algebra and Calculus: Essential for understanding how machine learning algorithms work under the hood.
3. Master Data Manipulation and Visualization
As a data analyst, you may already have experience in data visualization tools. However, data scientists need to go a step further by using Python and R for data manipulation.
Pandas & NumPy (Python): For handling large datasets efficiently.
Matplotlib & Seaborn: To create insightful visualizations.
Power BI & Tableau: If transitioning from analytics, leveraging these tools will be beneficial.
4. Learn Machine Learning Algorithms
Machine learning is the backbone of data science. You need to understand different types of machine learning models and their applications.
Supervised Learning: Regression and classification models (Linear Regression, Decision Trees, Random Forests, SVM, Neural Networks).
Unsupervised Learning: Clustering and dimensionality reduction techniques (K-Means, PCA, Autoencoders).
Deep Learning: Neural networks, CNNs, and RNNs for handling image and text data.
5. Work on Real-World Projects
Practical experience is crucial for a successful transition. Hands-on projects will help you apply your theoretical knowledge and build a strong portfolio.
Kaggle Competitions: Participate in Kaggle challenges to test your skills.
Open Source Contributions: Collaborate on GitHub projects.
Industry Projects: Apply for internships or freelancing gigs in data science.
6. Learn Big Data Technologies
Data scientists often work with massive datasets that require specialized tools for storage and processing.
Hadoop & Spark: For distributed computing and large-scale data processing.
Cloud Platforms (AWS, GCP, Azure): Cloud-based machine learning and data storage.
7. Build a Strong Portfolio and Resume
To stand out in the job market, showcase your data science projects on platforms like GitHub, Kaggle, and LinkedIn.
Create a Portfolio Website: Display your projects, blog posts, and certifications.
Write Technical Blogs: Share insights on data science topics on Medium or personal blogs.
Optimize Your Resume: Highlight your technical skills, certifications, and projects.
8. Obtain a Data Science Certification
Certifications validate your expertise and increase job opportunities.
Google Data Analytics Certificate
IBM Data Science Professional Certificate
AWS Certified Machine Learning Specialty
These certifications from top institutes offer some of the best training and will boost your credibility.
9. Network and Apply for Data Science Jobs
Networking plays a vital role in career transitions. Connect with data science professionals through LinkedIn, attend conferences, and join online communities.
Attend Meetups & Webinars: Engage with data science communities.
Leverage Job Portals: Apply on LinkedIn, Glassdoor, and Indeed.
Consider Internships: Entry-level data science roles or internships can help gain practical experience.
Conclusion
Transitioning from a data analyst to a data scientist is a challenging but rewarding journey. By following this roadmap—mastering programming, statistics, machine learning, and big data technologies—you can successfully shift into a data science role. Enrolling in the best courses and training programs will accelerate your learning and make you job-ready.
Remember, continuous learning and practical experience are key. Start today, work on projects, earn certifications, and network with industry professionals. Your dream job as a data scientist is just a few steps away.
0 notes
Text
PowerApps Training | Power Automate Training
PowerApps Search Function: Using 'Contains' for Better Results

PowerApps Training, The PowerApps Search Function is an essential tool for building efficient and user-friendly applications. This function empowers developers and users to find data quickly and easily by providing flexibility in how they search within an app. One of the most powerful features of the PowerApps Search Function is its ability to incorporate the Contains operator, which allows for partial matches and delivers more relevant search results.
In this article, we will explore how the PowerApps Search Function works, its benefits, and step-by-step guidance on using the Contains operator effectively. Whether you're a beginner or a seasoned developer, you'll discover actionable insights to enhance your PowerApps applications. Power Automate Training
What Is the PowerApps Search Function?
The PowerApps Search Function is used to filter records in a data source based on search criteria entered by the user. It provides a simple and effective way to build search capabilities into your app. For instance, users can type a keyword in a search bar, and the app will display matching results from a table, collection, or connected data source.
The PowerApps Search Function is particularly valuable because it supports case-insensitive searches, making it easier for users to find what they need without worrying about capitalization. Additionally, when combined with the Contains operator, it becomes even more powerful, allowing for partial matches and broader search possibilities.
Why Use the 'Contains' Operator with PowerApps Search Function?
The Contains operator enhances the flexibility of the PowerApps Search Function. Instead of requiring an exact match for a search term, Contains lets users search for records that include the term anywhere in the field. This functionality is ideal for scenarios where users might only know part of a name, description, or keyword. PowerApps Training
For example, imagine a scenario where you're building an app to search a customer database. A user searching for "Smith" can find records like "John Smith" or "Smithson Enterprises" without needing to type the exact match.
Some key benefits of using the Contains operator with the PowerApps Search Function include:
Improved User Experience: Users can find results even with incomplete information.
Faster Data Retrieval: Partial matches save time and reduce the frustration of unsuccessful searches.
Enhanced Flexibility: Works seamlessly across different types of data fields, such as names, descriptions, and IDs.
How to Use 'Contains' with PowerApps Search Function
Here’s a step-by-step guide to implementing the Contains operator with the PowerApps Search Function in your application:
Step 1: Set Up Your Data Source
First, ensure that your app is connected to a data source. This could be a SharePoint list, Excel table, or SQL database. For demonstration purposes, let's assume you're working with a collection named CustomerData. Power Automate Training
Step 2: Add a Search Bar
Add a Text Input control to your app and name it txtSearch. This will serve as the search bar where users can input their search terms.
Step 3: Configure the Search Functionality
To enable the PowerApps Search Function in your app, begin by setting up a mechanism for users to enter their search terms, such as a search bar or text input field. Link this search bar to your data source and specify the fields you want users to search through, such as names, emails, or phone numbers. This ensures that the app dynamically filters and displays relevant results based on the user’s input.
Step 4: Refine with 'Contains' for Partial Matches
To make your search feature more robust, utilize the Contains operator. This ensures that users can retrieve results even if they only provide partial information. For instance, a search for a partial name or keyword will match records containing that term anywhere in the relevant fields. By applying this approach, your app delivers more accurate and inclusive search results, enhancing the overall user experience.
Step 5: Test and Refine
Run your app and test the search functionality by entering different keywords. Adjust the fields in the formula as needed to optimize the search experience for your users.
Best Practices for Using PowerApps Search Function
To maximize the effectiveness of the PowerApps Search Function, consider these best practices:
Optimize Data Sources: Ensure your data sources are indexed and structured efficiently to improve search performance.
Limit Search Scope: Avoid searching across too many fields simultaneously, as this can slow down performance.
Provide Clear Instructions: Add placeholders or tooltips to the search bar to guide users on how to use the search function effectively.
Enhance Results Display: Use filters and sorting options to make search results more user-friendly.
Handle Empty Results: Add a message or visual indicator to inform users when no results are found.
Real-World Applications of PowerApps Search Function
The PowerApps Search Function is widely used across various industries. Here are a few examples:
Customer Relationship Management (CRM): Quickly search for customer details by name, email, or phone number.
Inventory Management: Find products based on partial names or descriptions.
Employee Directory: Locate employees in a database using their first or last name.
Event Management: Search for attendees based on registration details.
These applications demonstrate the versatility of the PowerApps Search Function, particularly when paired with the Contains operator.
Common Challenges and How to Overcome Them
While the PowerApps Search Function is powerful, it does come with some challenges:
Performance Issues with Large Data Sets: Searching large data sources can slow down app performance. Solution: Use delegable data sources and optimize your queries.
Complex Search Requirements: Advanced filtering may require combining multiple functions, such as Search, Filter, and Contains. Solution: Plan your formulas carefully and test extensively.
Case Sensitivity in Non-Delegable Functions: Although Search is case-insensitive, combining it with other functions may introduce case-sensitivity. Solution: Use Lower or Upper to normalize text.
Conclusion
The PowerApps Search Function is a game-changer for building dynamic, user-friendly apps. By integrating the Contains operator, you can elevate your app’s search capabilities, enabling users to find data more easily and efficiently. Whether you’re developing a CRM, an inventory tracker, or an employee directory, mastering the PowerApps Search Function is a must for delivering a superior user experience.
Start exploring the possibilities of the PowerApps Search Function today and see how it transforms your application’s functionality!
Visualpath is the Leading and Best Institute for learning in Hyderabad. We provide PowerApps and Power Automate Training. You will get the best course at an affordable cost.
Attend Free Demo
Call on – +91-9989971070
Blog: https://toppowerautomatetraining.blogspot.com/
What’s App: https://www.whatsapp.com/catalog/919989971070/
Visit: https://www.visualpath.in/online-powerapps-training.html
#PowerApps Training#Power Automate Training#PowerApps Training in Hyderabad#PowerApps Online Training#Microsoft PowerApps Training#PowerApps Training Course#PowerApps and Power Automate Training#Microsoft PowerApps Training Courses
1 note
·
View note
Text
Database change management tools are of great help to developers and database administrators. These tools increase the efficiency of their work. Earlier database administrators used command lines to delete, create and edit databases. However now with the introduction of Database Change Management tools, the work load of the DBA’s has reduced considerably. Below are given different types of open source database change management tools which are of great help to the DBA’s: LIQUIBASE Liquibase is an open source (Apache 2.0 Licensed), database-independent library for tracking, managing and applying database changes. LIQUIBASE is used by developers in locating and making amendments in the database. The track of all these changes are maintained in an XML file (database changelog file) which serves to overview the list of changes made. It is compatible with any database which java can easily connect to. Key Features Efficiently manage multiple databases Extensible to make changes Able to keep a track record of database changes Execution can take place through Maven, command line, Ant etc. Download is available at https://www.liquibase.org/download DBDeploy Designed by a team of professionals at “Thoughworks”, this database change management tool is basically used by developers to manage and enhance their database designs. It is much more useful for those who refactor their database more often. Dbdeploy has employed java for its code construction and unifies with Sybase and Hypersonic SQL databases, Apache Ant build tool supporting Oracle. Key Features Simple to use Works well with Ant Download is available at http://code.google.com/p/dbdeploy/downloads/list Ruckusing This database tool is a frame of reference written in PHP5. Its use is to create and manage “database migrations”. These “database migrations” are files that define the present status of a database like its indexes, columns etc. The salient feature of this database is that multiple users can simultaneously work on the same application. In case of a crash by an individual the other users shall not be disrupted. The idea of the framework was influenced from the migration system built into Ruby on Rails. Any one who is familiar with Migrations in RoR will be able to use this quickly Key Features Portability: The migration files are initially written in PHP5 which are further translated to appropriate SQL during runtime. Thus providing an option of supporting any RDBMS with a single migration file. The ability to move (up and down) to particular migration state Download is available at DBSource Tools This database management tool is in there in form of a GUI service. Its use is to bring SQL server database under source control. Key Features Can be used to compare schemas Strong database scripter Download is available at Nextep Open Designer This IDE is used as a remedial measure for the deployment and development of the database as well as automating you test processes and your deployment. This software is available for free and its installation has many advantages. NeXtep Open Designer uses a centralized version control repository to track any change you make on your database model, source code (PL/SQL, T-SQL, etc.) and reference data. This repository is a simple database schema that can be automatically deployed to any supported database. Key Features Ease of merging database during development Helps in integrating deployment processes Download is available at http://www.nextep-softwares.com/index.php/products Tasks like maintaining and updating the relational databases are done by these tools very quickly and efficiently. These tools also help in maintaining the complex projects thus making the task easier for developers. Thus if you wish to increase your efficiency then these Database Management Tools are highly recommended. Hope you found this list useful! What are the tools you have used for database management? Please don't forget to share with us in comments.
Article Updates Article Updated on September 2021. Some HTTP links are updated to HTTPS. Updated broken links with latest URLs. Some minor text updates done. Content validated and updated for relevance in 2021.
0 notes
Text
Mastering SQL Injection (SQLi) Protection for Symfony with Examples
Understanding and Preventing SQL Injection (SQLi) in Symfony Applications
SQL Injection (SQLi) remains one of the most common and damaging vulnerabilities affecting web applications. This guide will dive into what SQLi is, why Symfony developers should be aware of it, and practical, example-based strategies to prevent it in Symfony applications.

What is SQL Injection (SQLi)?
SQL Injection occurs when attackers can insert malicious SQL code into a query, allowing them to access, alter, or delete database data. For Symfony apps, this can happen if inputs are not properly handled. Consider the following unsafe SQL query:
php
$query = "SELECT * FROM users WHERE username = '" . $_POST['username'] . "' AND password = '" . $_POST['password'] . "'";
Here, attackers could input SQL code as the username or password, potentially gaining unauthorized access.
How to Prevent SQL Injection in Symfony
Symfony provides tools that, when used correctly, can prevent SQL Injection vulnerabilities. Here are the best practices, with examples, to secure your Symfony app.
1. Use Prepared Statements (Example Included)
Prepared statements ensure SQL queries are safely constructed by separating SQL code from user inputs. Here’s an example using Symfony's Doctrine ORM:
php
// Safe SQL query using Doctrine $repository = $this->getDoctrine()->getRepository(User::class); $user = $repository->findOneBy([ 'username' => $_POST['username'], 'password' => $_POST['password'] ]);
Doctrine’s findOneBy() automatically prepares statements, preventing SQL Injection.
2. Validate and Sanitize Input Data
Input validation restricts the type and length of data users can input. Symfony’s Validator component makes this easy:
php
use Symfony\Component\Validator\Validation; use Symfony\Component\Validator\Constraints as Assert; $validator = Validation::createValidator(); $input = $_POST['username']; $violations = $validator->validate($input, [ new Assert\Length(['max' => 20]), new Assert\Regex(['pattern' => '/^[a-zA-Z0-9_]+$/']) ]); if (count($violations) > 0) { // Handle invalid input }
In this example, only alphanumeric characters are allowed, and the input length is limited to 20 characters, reducing SQL Injection risks.
3. Use Doctrine’s Query Builder for Safe Queries
The Symfony Query Builder simplifies creating dynamic queries while automatically escaping input data. Here’s an example:
php
$qb = $this->createQueryBuilder('u'); $qb->select('u') ->from('users', 'u') ->where('u.username = :username') ->setParameter('username', $_POST['username']); $query = $qb->getQuery(); $result = $query->getResult();
By using setParameter(), Symfony binds the input parameter safely, blocking potential injection attacks.
Using Free Tools for Vulnerability Assessment
To check your application’s security, visit our Free Tools page. Here’s a snapshot of the free tools page where you can scan your website for SQL Injection vulnerabilities:

These tools help you identify security issues and provide guidance on securing your Symfony application.
Example: Vulnerability Assessment Report
Once you’ve completed a vulnerability scan, you’ll receive a detailed report outlining detected issues and recommended fixes. Here’s an example screenshot of a vulnerability assessment report generated by our free tool:

This report gives insights into potential SQL Injection vulnerabilities and steps to improve your app’s security.
Additional Resources
For more guidance on web security and SQL Injection prevention, check out our other resources:
Pentest Testing – Get expert penetration testing services.
Cyber Rely – Access comprehensive cybersecurity resources.
Conclusion
SQL Injection vulnerabilities can be effectively mitigated with the right coding practices. Symfony’s built-in tools like Doctrine, the Query Builder, and the Validator are valuable resources for safeguarding your application. Explore our free tools and vulnerability assessments to strengthen your Symfony app’s security today!
#cybersecurity#sql#sqlserver#penetration testing#pentesting#cyber security#the security breach show#data security#security
1 note
·
View note
Text
Quotes from the book Data Science on AWS
Data Science on AWS
Antje Barth, Chris Fregly
As input data, we leverage samples from the Amazon Customer Reviews Dataset [https://s3.amazonaws.com/amazon-reviews-pds/readme.html]. This dataset is a collection of over 150 million product reviews on Amazon.com from 1995 to 2015. Those product reviews and star ratings are a popular customer feature of Amazon.com. Star rating 5 is the best and 1 is the worst. We will describe and explore this dataset in much more detail in the next chapters.
*****
Let’s click Create Experiment and start our first Autopilot job. You can observe the progress of the job in the UI as shown in Figure 1-11.
--
Amazon AufotML experiments
*****
...When the Feature Engineering stage starts, you will see SageMaker training jobs appearing in the AWS Console as shown in Figure 1-13.
*****
Autopilot built to find the best performing model. You can select any of those training jobs to view the job status, configuration, parameters, and log files.
*****
The Model Tuning creates a SageMaker Hyperparameter tuning job as shown in Figure 1-15. Amazon SageMaker automatic model tuning, also known as hyperparameter tuning (HPT), is another functionality of the SageMaker service.
*****
You can find an overview of all AWS instance types supported by Amazon SageMaker and their performance characteristics here: https://aws.amazon.com/sagemaker/pricing/instance-types/. Note that those instances start with ml. in their name.
Optionally, you can enable data capture of all prediction requests and responses for your deployed model. We can now click on Deploy model and watch our model endpoint being created. Once the endpoint shows up as In Service
--
Once Autopilot find best hyperpharameters you can deploy them to save for later
*****
Here is a simple Python code snippet to invoke the endpoint. We pass a sample review (“I loved it!”) and see which star rating our model chooses. Remember, star rating 1 is the worst and star rating 5 is the best.
*****
If you prefer to interact with AWS services in a programmatic way, you can use the AWS SDK for Python boto3 [https://boto3.amazonaws.com/v1/documentation/api/latest/index.html], to interact with AWS services from your Python development environment.
*****
In the next section, we describe how you can run real-time predictions from within a SQL query using Amazon Athena.
*****
Amazon Comprehend. As input data, we leverage a subset of Amazon’s public customer reviews dataset. We want Amazon Comprehend to classify the sentiment of a provided review. The Comprehend UI is the easiest way to get started. You can paste in any text and Comprehend will analyze the input in real-time using the built-in model. Let’s test this with a sample product review such as “I loved it! I will recommend this to everyone.” as shown in Figure 1-23.
*****
mprehend Custom is another example of automated machine learning that enables the practitioner to fine-tune Comprehend’s built-in model to a specific datase
*****
We will introduce you to Amazon Athena and show you how to leverage Athena as an interactive query service to analyze data in S3 using standard SQL, without moving the data. In the first step, we will register the TSV data in our S3 bucket with Athena, and then run some ad-hoc queries on the dataset. We will also show how you can easily convert the TSV data into the more query-optimized, columnar file format Apache Parquet.
--
S3 deki datayı her zaman parquet e çevir
*****
One of the biggest advantages of data lakes is that you don’t need to pre-define any schemas. You can store your raw data at scale and then decide later in which ways you need to process and analyze it. Data Lakes may contain structured relational data, files, and any form of semi-structured and unstructured data. You can also ingest data in real time.
*****
Each of those steps involves a range of tools and technologies, and while you can build a data lake manually from the ground up, there are cloud services available to help you streamline this process, i.e. AWS Lake Formation.
Lake Formation helps you to collect and catalog data from databases and object storage, move the data into your Amazon S3 data lake, clean and classify your data using machine learning algorithms, and secure access to your sensitive data.
*****
From a data analysis perspective, another key benefit of storing your data in Amazon S3 is, that it shortens the “time to insight’ dramatically, as you can run ad-hoc queries directly on the data in S3, and you don’t have to go through complex ETL (Extract-Transform-Load) processes and data pipeli
*****
Amazon Athena is an interactive query service that makes it easy to analyze data in Amazon S3 using standard SQL. Athena is serverless, so you don’t need to manage any infrastructure, and you only pay for the queries you run.
*****
With Athena, you can query data wherever it is stored (S3 in our case) without needing to move the data to a relational database.
*****
Athena and Redshift Spectrum can use to locate and query data.
*****
Athena queries run in parallel over a dynamic, serverless cluster which makes Athena extremely fast -- even on large datasets. Athena will automatically scale the cluster depending on the query and dataset -- freeing the user from worrying about these details.
*****
Athena is based on Presto, an open source, distributed SQL query engine designed for fast, ad-hoc data analytics on large datasets. Similar to Apache Spark, Presto uses high RAM clusters to perform its queries. However, Presto does not require a large amount of disk as it is designed for ad-hoc queries (vs. automated, repeatable queries) and therefore does not perform the checkpointing required for fault-tolerance.
*****
Apache Spark is slower than Athena for many ad-hoc queries.
*****
For longer-running Athena jobs, you can listen for query-completion events using CloudWatch Events. When the query completes, all listeners are notified with the event details including query success status, total execution time, and total bytes scanned.
*****
With a functionality called Athena Federated Query, you can also run SQL queries across data stored in relational databases (such as Amazon RDS and Amazon Aurora), non-relational databases (such as Amazon DynamoDB), object storage (Amazon S3), and custom data sources. This gives you a unified analytics view across data stored in your data warehouse, data lake and operational databases without the need to actually move the data.
*****
You can access Athena via the AWS Management Console, an API, or an ODBC or JDBC driver for programmatic access. Let’s have a look at how to use Amazon Athena via the AWS Management Console.
*****
When using LIMIT, you can better-sample the rows by adding TABLESAMPLE BERNOULLI(10) after the FROM. Otherwise, you will always return the data in the same order that it was ingested into S3 which could be skewed towards a single product_category, for example. To reduce code clutter, we will just use LIMIT without TABLESAMPLE.
*****
In a next step, we will show you how you can easily convert that data now into the Apache Parquet columnar file format to improve the query performance. Parquet is optimized for columnar-based queries such as counts, sums, averages, and other aggregation-based summary statistics that focus on the column values vs. row information.
*****
selected for DATABASE and then choose “New Query” and run the following “CREATE TABLE AS” (short CTAS) SQL statement:
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS dsoaws.amazon_reviews_parquet
WITH (format = 'PARQUET', external_location = 's3://data-science-on-aws/amazon-reviews-pds/parquet', partitioned_by = ARRAY['product_category']) AS
SELECT marketplace,
*****
One of the fundamental differences between data lakes and data warehouses is that while you ingest and store huge amounts of raw, unprocessed data in your data lake, you normally only load some fraction of your recent data into your data warehouse. Depending on your business and analytics use case, this might be data from the past couple of months, a year, or maybe the past 2 years. Let’s assume we want to have the past 2 years of our Amazon Customer Reviews Dataset in a data warehouse to analyze year-over-year customer behavior and review trends. We will use Amazon Redshift as our data warehouse for this.
*****
Amazon Redshift is a fully managed data warehouse which allows you to run complex analytic queries against petabytes of structured data. Your queries are distributed and parallelized across multiple nodes. In contrast to relational databases which are optimized to store data in rows and mostly serve transactional applications, Redshift implements columnar data storage which is optimized for analytical applications where you are mostly interested in the data within the individual columns.
*****
Redshift Spectrum, which allows you to directly execute SQL queries from Redshift against exabytes of unstructured data in your Amazon S3 data lake without the need to physically move the data. Amazon Redshift Spectrum automatically scales the compute resources needed based on how much data is being received, so queries against Amazon S3 run fast, regardless of the size of your data.
*****
We will use Amazon Redshift Spectrum to access our data in S3, and then show you how you can combine data that is stored in Redshift with data that is still in S3.
This might sound similar to the approach we showed earlier with Amazon Athena, but note that in this case we show how your Business Intelligence team can enrich their queries with data that is not stored in the data warehouse itself.
*****
So with just one command, we now have access and can query our S3 data lake from Amazon Redshift without moving any data into our data warehouse. This is the power of Redshift Spectrum.
But now, let’s actually copy some data from S3 into Amazon Redshift. Let’s pull in customer reviews data from the year 2015.
*****
You might ask yourself now, when should I use Athena, and when should I use Redshift? Let’s discuss.
*****
Amazon Athena should be your preferred choice when running ad-hoc SQL queries on data that is stored in Amazon S3. It doesn’t require you to set up or manage any infrastructure resources, and you don’t need to move any data. It supports structured, unstructured, and semi-structured data. With Athena, you are defining a “schema on read” -- you basically just log in, create a table and you are good to go.
Amazon Redshift is targeted for modern data analytics on large, peta-byte scale, sets of structured data. Here, you need to have a predefined “schema on write”. Unlike serverless Athena, Redshift requires you to create a cluster (compute and storage resources), ingest the data and build tables before you can start to query, but caters to performance and scale. So for any highly-relational data with a transactional nature (data gets updated), workloads which involve complex joins, and latency requirements to be sub-second, Redshift is the right choice.
*****
But how do you know which objects to move? Imagine your S3 data lake has grown over time, and you might have billions of objects across several S3 buckets in S3 Standard storage class. Some of those objects are extremely important, while you haven’t accessed others maybe in months or even years. This is where S3 Intelligent-Tiering comes into play.
Amazon S3 Intelligent-Tiering, automatically optimizes your storage cost for data with changing access patterns by moving objects between the frequent-access tier optimized for frequent use of data, and the lower-cost infrequent-access tier optimized for less-accessed data.
*****
Amazon Athena offers ad-hoc, serverless SQL queries for data in S3 without needing to setup, scale, and manage any clusters.
Amazon Redshift provides the fastest query performance for enterprise reporting and business intelligence workloads, particularly those involving extremely complex SQL with multiple joins and subqueries across many data sources including relational databases and flat files.
*****
To interact with AWS resources from within a Python Jupyter notebook, we leverage the AWS Python SDK boto3, the Python DB client PyAthena to connect to Athena, and SQLAlchemy) as a Python SQL toolkit to connect to Redshift.
*****
easy-to-use business intelligence service to build visualizations, perform ad-hoc analysis, and build dashboards from many data sources - and across many devices.
*****
We will also introduce you to PyAthena, the Python DB Client for Amazon Athena, that enables us to run Athena queries right from our notebook.
*****
There are different cursor implementations that you can use. While the standard cursor fetches the query result row by row, the PandasCursor will first save the CSV query results in the S3 staging directory, then read the CSV from S3 in parallel down to your Pandas DataFrame. This leads to better performance than fetching data with the standard cursor implementation.
*****
We need to install SQLAlchemy, define our Redshift connection parameters, query the Redshift secret credentials from AWS Secret Manager, and obtain our Redshift Endpoint address. Finally, create the Redshift Query Engine.
# Ins
*****
Create Redshift Query Engine
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
engine = create_engine('postgresql://{}:{}@{}:{}/{}'.format(redshift_username, redshift_pw, redshift_endpoint_address, redshift_port, redshift_database))
*****
Detect Data Quality Issues with Apache Spark
*****
Data quality can halt a data processing pipeline in its tracks. If these issues are not caught early, they can lead to misleading reports (ie. double-counted revenue), biased AI/ML models (skewed towards/against a single gender or race), and other unintended data products.
To catch these data issues early, we use Deequ, an open source library from Amazon that uses Apache Spark to analyze data quality, detect anomalies, and even “notify the Data Scientist at 3am” about a data issue. Deequ continuously analyzes data throughout the complete, end-to-end lifetime of the model from feature engineering to model training to model serving in production.
*****
Learning from run to run, Deequ will suggest new rules to apply during the next pass through the dataset. Deequ learns the baseline statistics of our dataset at model training time, for example - then detects anomalies as new data arrives for model prediction. This problem is classically called “training-serving skew”. Essentially, a model is trained with one set of learned constraints, then the model sees new data that does not fit those existing constraints. This is a sign that the data has shifted - or skewed - from the original distribution.
*****
Since we have 130+ million reviews, we need to run Deequ on a cluster vs. inside our notebook. This is the trade-off of working with data at scale. Notebooks work fine for exploratory analytics on small data sets, but not suitable to process large data sets or train large models. We will use a notebook to kick off a Deequ Spark job on a cluster using SageMaker Processing Jobs.
*****
You can optimize expensive SQL COUNT queries across large datasets by using approximate counts.
*****
HyperLogLogCounting is a big deal in analytics. We always need to count users (daily active users), orders, returns, support calls, etc. Maintaining super-fast counts in an ever-growing dataset can be a critical advantage over competitors.
Both Redshift and Athena support HyperLogLog (HLL), a type of “cardinality-estimation” or COUNT DISTINCT algorithm designed to provide highly accurate counts (<2% error) in a small fraction of the time (seconds) requiring a tiny fraction of the storage (1.2KB) to store 130+ million separate counts.
*****
Existing data warehouses move data from storage nodes to compute nodes during query execution. This requires high network I/O between the nodes - and reduces query performance.
Figure 3-23 below shows a traditional data warehouse architecture with shared, centralized storage.
*****
certain “latent” features hidden in our data sets and not immediately-recognizable by a human. Netflix’s recommendation system is famous for discovering new movie genres beyond the usual drama, horror, and romantic comedy. For example, they discovered very specific genres such as “Gory Canadian Revenge Movies,” “Sentimental Movies about Horses for Ages 11-12,” “
*****
Figure 6-2 shows more “secret” genres discovered by Netflix’s Viewing History Service - code named, “VHS,” like the popular video tape format from the 80’s and 90’s.
*****
Feature creation combines existing data points into new features that help improve the predictive power of your model. For example, combining review_headline and review_body into a single feature may lead to more-accurate predictions than using them separately.
*****
Feature transformation converts data from one representation to another to facilitate machine learning. Transforming continuous values such as a timestamp into categorical “bins” such as hourly, daily, or monthly helps to reduce dimensionality. Two common statistical feature transformations are normalization and standardization. Normalization scales all values of a particular data point between 0 and 1, while standardization transforms the values to a mean of 0 and standard deviation of 1. These techniques help reduce the impact of large-valued data points such as number of reviews (represented in 1,000’s) over small-valued data points such as helpful_votes (represented in 10’s.) Without these techniques, the mod
*****
One drawback to undersampling is that your training dataset size is sampled down to the size of the smallest category. This can reduce the predictive power of your trained models. In this example, we reduced the number of reviews by 65% from approximately 100,000 to 35,000.
*****
Oversampling will artificially create new data for the under-represented class. In our case, star_rating 2 and 3 are under-represented. One common oversampling technique is called Synthetic Minority Oversampling Technique (SMOTE). Oversampling techniques use statistical methods such as interpolation to generate new data from your current data. They tend to work better when you have a larger data set, so be careful when using oversampling on small datasets with a low number of minority class examples. Figure 6-10 shows SMOTE generating new examples for the minority class to improve the imbalance.
*****
Each of the three phases should use a separate and independent dataset - otherwise “leakage” may occur. Leakage happens when data is leaked from one phase of modeling into another through the splits. Leakage can artificially inflate the accuracy of your model.
Time-series data is often prone to leakage across splits. Companies often want to validate a new model using “back-in-time” historical information before pushing the model to production. When working with time-series data, make sure your model does not peak into the future accidentally. Otherwise, these models may appear more accurate than they really are.
*****
We will use TensorFlow and a state-of-the-art Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Natural Language Understanding (NLU) neural network architecture called BERT. Unlike previous generations of NLP models such as Word2Vec, BERT captures the bi-directional (left-to-right and right-to-left) context of each word in a sentence. This allows BERT to learn different meanings of the same word across different sentences. For example, the meaning of the word “bank” is different between these two sentences: “A thief stole money from the bank vault” and “Later, he was arrested while fishing on a river bank.”
For each review_body, we use BERT to create a feature vector within a previously-learned, high-dimensional vector space of 30,000 words or “tokens.” BERT learned these tokens by training on millions of documents including Wikipedia and Google Books.
Let’s use a variant of BERT called DistilBert. DistilBert is a light-weight version of BERT that is 60% faster, 40% smaller, and preserves 97% of BERT’s language understanding capabilities. We use a popular Python library called Transformers to perform the transformation.
*****
Feature stores can cache “hot features” into memory to reduce model-training times. A feature store can provide governance and access control to regulate and audit our features. Lastly, a feature store can provide consistency between model training and model predicting by ensuring the same features for both batch training and real-time predicting.
Customers have implemented feature stores using a combination of DynamoDB, ElasticSearch, and S3. DynamoDB and ElasticSearch track metadata such as file format (ie. csv, parquet), BERT-specific data (ie. maximum sequence length), and other summary statistics (ie. min, max, standard deviation). S3 stores the underlying features such as our generated BERT embeddings. This feature store reference architecture is shown in Figure 6-22.
*****
Our training scripts almost always include pip installing Python libraries from PyPi or downloading pre-trained models from third-party model repositories (or “model zoo’s”) on the internet. By creating dependencies on external resources, your training job is now at the mercy of these third-party services. If one of these services is temporarily down, your training job may not start.
To improve availability, it is recommended that we reduce as many external dependencies as possible by copying these resources into your Docker images - or into your own S3 bucket. This has the added benefit of reducing network utilization and starting our training jobs faster.
*****
Bring Your Own Container
The most customizable option is “bring your own container” (BYOC). This option lets you build and deploy your own Docker container to SageMaker. This Docker container can contain any library or framework. While we maintain complete control over the details of the training script and its dependencies, SageMaker manages the low-level infrastructure for logging, monitoring, environment variables, S3 locations, etc. This option is targeted at more specialized or systems-focused machine learning folks.
*****
GloVe goes one step further and uses recurrent neural networks (RNNs) to encode the global co-occurrence of words vs. Word2Vec’s local co-occurence of words. An RNN is a special type of neutral network that learns and remembers longer-form inputs such as text sequences and time-series data.
FastText continues the innovation and builds word embeddings using combinations of lower-level character embeddings using character-level RNNs. This character-level focus allows FastText to learn non-English language models with relatively small amounts of data compared to other models. Amazon SageMaker offers a built-in, pay-as-you-go SageMaker algorithm called BlazingText which is an implementation of FastText optimized for AWS. This algorithm was shown in the Built-In Algorithms section above.
*****
ELMo preserves the trained model and uses two separate Long-Short Term Memory (LSTM) networks: one to learn from left-to-right and one to learn from right-to-left. Neither LSTM uses both the previous and next words at the same time, however. Therefore ELMo does not learn a true bidirectional contextual representation of the words and phrases in the corpus, but it performs very well nonetheless.
*****
Without this bi-directional attention, an algorithm would potentially create the same embedding for the word bank for the following two(2) sentences: “A thief stole money from the bank vault” and “Later, he was arrested while fishing on a river bank.” Note that the word bank has a different meaning in each sentence. This is easy for humans to distinguish because of our life-long, natural “pre-training”, but this is not easy for a machine without similar pre-training.
*****
To be more concrete, BERT is trained by forcing it to predict masked words in a sentence. For example, if we feed in the contents of this book, we can ask BERT to predict the missing word in the following sentence: “This book is called Data ____ on AWS.” Obviously, the missing word is “Science.” This is easy for a human who has been pre-trained on millions of documents since birth, but not easy fo
*****
Neural networks are designed to be re-used and continuously trained as new data arrives into the system. Since BERT has already been pre-trained on millions of public documents from Wikipedia and the Google Books Corpus, the vocabulary and learned representations are transferable to a large number of NLP and NLU tasks across a wide variety of domains.
Training BERT from scratch requires a lot of data and compute, it allows BERT to learn a representation of the custom dataset using a highly-specialized vocabulary. Companies like LinkedIn have pre-trained BERT from scratch to learn language representations specific to their domain including job titles, resumes, companies, and business news. The default pre-trained BERT models were not good enough for NLP/NLU tasks. Fortunately, LinkedIn has plenty of data and compute
*****
The choice of instance type and instance count depends on your workload and budget. Fortunately AWS offers many different instance types including AI/ML-optimized instances with terabytes of RAM and gigabits of network bandwidth. In the cloud, we can easily scale our training job to tens, hundreds, or even thousands of instances with just one line of code.
Let’s select 3 instances of the powerful p3.2xlarge - each with 8 CPUs, 61GB of CPU RAM, 1 Nvidia Volta V100’s GPU processor, and 16GB of GPU RAM. Empirically, we found this combination to perform well with our specific training script and dataset - and within our budget for this task.
instance_type='ml.p3.2xlarge'
instance_count=3
*****
TIP: You can specify instance_type='local' to run the script either inside your notebook or on your local laptop. In both cases, your script will execute inside of the same open source SageMaker Docker container that runs in the managed SageMaker service. This lets you test locally before incurring any cloud cost.
*****
Also, it’s important to choose parallelizable algorithms that benefit from multiple cluster instances. If your algorithm is not parallelizable, you should not add more instances as they will not be used. And adding too many instances may actually slow down your training job by creating too much communication overhead between the instances. Most neural network-based algorithms like BERT are parallelizable and benefit from a distributed cluster.
0 notes
Text
Migrating from SQL Server to Snowflake Essential Steps and Benefits
Transitioning from SQL Server to Snowflake can significantly enhance your data management capabilities. Snowflake's cloud-native architecture offers numerous advantages, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency, making it a popular choice for modern data warehousing needs. This article outlines the essential steps and benefits of migrating from SQL Server to Snowflake.
Key Steps for Migration
1. Initial Assessment and Planning
Start with a thorough assessment of your existing SQL Server environment. Identify the databases, tables, and other objects that need to be migrated. Understand the data volume, dependencies, and specific requirements of your applications. Develop a comprehensive migration plan that includes timelines, resources, and risk mitigation strategies.
2. Choosing the Right Migration Tools
Select migration tools that facilitate a smooth transition from SQL Server to Snowflake. Tools such as Azure Data Factory, Matillion, and Fivetran can help automate the extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL) processes. These tools ensure data integrity and minimize downtime during the migration.

3. Schema Conversion
SQL Server and Snowflake have different schema structures. Use schema conversion tools to translate SQL Server schemas into Snowflake-compatible formats. Pay attention to data types, indexing, and partitioning strategies to optimize performance in Snowflake.
4. Data Transformation and Migration
Transform your data to align with Snowflake’s architecture. This might involve data cleansing, reformatting, and converting stored procedures and T-SQL code into Snowflake’s SQL dialect. Leverage Snowflake’s capabilities, such as support for semi-structured data and time travel features, to enhance your data operations.
5. Testing and Validation
Perform thorough testing and validation to ensure that the data has been accurately migrated and that all applications function as expected. Validate data integrity, check for any discrepancies, and conduct performance testing to ensure that Snowflake meets your performance requirements.
6. Security and Compliance
Implement robust security measures to protect your data during and after the migration. Ensure that access controls, encryption, and compliance requirements are met in the Snowflake environment. Snowflake provides extensive security features, including role-based access control and end-to-end encryption.
Benefits of Migrating to Snowflake
1. Scalability and Performance
Snowflake’s architecture allows for automatic scaling of compute resources to handle varying workloads efficiently. This elasticity ensures consistent performance without manual intervention, making it ideal for businesses with growing and fluctuating data needs.
2. Cost Efficiency
With Snowflake’s pay-as-you-go pricing model, you only pay for the storage and compute resources you use. This can lead to significant cost savings, especially for organizations with variable data workloads. Snowflake's separation of storage and compute allows you to optimize resource usage and reduce costs.
3. Simplified Data Management
Snowflake offers a fully managed service, reducing the burden of database administration. Automatic updates, maintenance, and performance tuning are handled by Snowflake, allowing your IT team to focus on more strategic tasks and innovations.
4. Advanced Analytics Capabilities
Snowflake supports diverse data types and integrates seamlessly with various data analytics tools. This enables advanced analytics and machine learning applications, allowing you to gain deeper insights from your data. Snowflake’s support for semi-structured data like JSON, Avro, and Parquet enhances your analytical capabilities.
5. Enhanced Data Sharing and Collaboration
Snowflake’s secure data sharing capabilities facilitate seamless collaboration across departments and with external partners. Real-time data sharing without the need for complex ETL processes improves efficiency and enables better decision-making.
6. Robust Security Features
Snowflake incorporates comprehensive security measures, including end-to-end encryption, role-based access control, and detailed auditing capabilities. These features ensure that your data remains secure and compliant with regulatory standards.
1 note
·
View note
Text
So, I've eliminated a few paths already. One has nice examples that the author says are scripts. They're not Batch commands. If they're PowerShell, I don't have the right module (and it doesn't look right to my untrained eye). So what are they? Another was supposedly learning to use ScriptDOM, but no explanation of what to create is included. Maybe I'm too inexperienced to understand some stuff, but if you don't include at least a file type I'm fairly sure you skipped something.
So I'm trying this. It's worth a shot. First step, have a database project in VS. Uhm... I've never done that. I know why we should. But my work has a history of not requiring programmers to document what we do on production systems. Finally got the server admins doing it a while ago, but folks like me live dangerously. Grumble.
So - step 1, create a database. It's not a listed step, but apparently you don't do the creation in VS. There's no step for it in the template listing at least.
So instead I'm doing https://medium.com/hitachisolutions-braintrust/create-your-first-visual-studio-database-project-e6c22e45145b
Step one: in SSMS run the command:
CREATE DATABASE TCommon
T for temporary, and Common is a database I've already got going. It's for non-secure tools/programs/etc. that any of the other databases should be able to access.
Now to start up VS 2022. We begin a new project and search for database templates.
Clear the checkbox for putting the solution and project in the same directory, and give an overarching name to the solution. That way you can have multiple database projects worked on inside of one solution.
Next, we import the blank database so we have a test bed based off what is in production. Right click on the solution name, select Import, then Database.
The import database wizard looks like this after the connection is set.
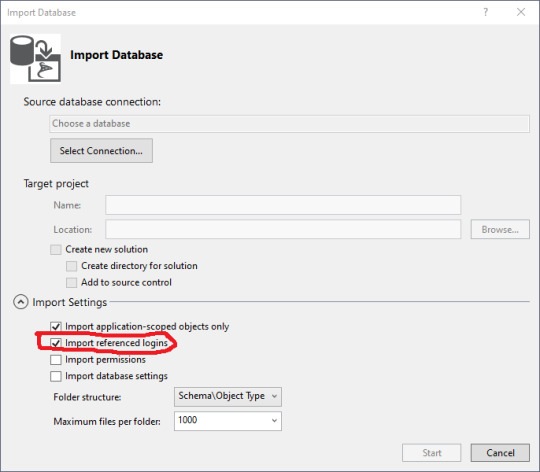
Blackburn suggests that you turn off the importation of referenced logins so you don't accidentally alter permissions. Sound strategy.
Then you can click on the "Select Connection" button.
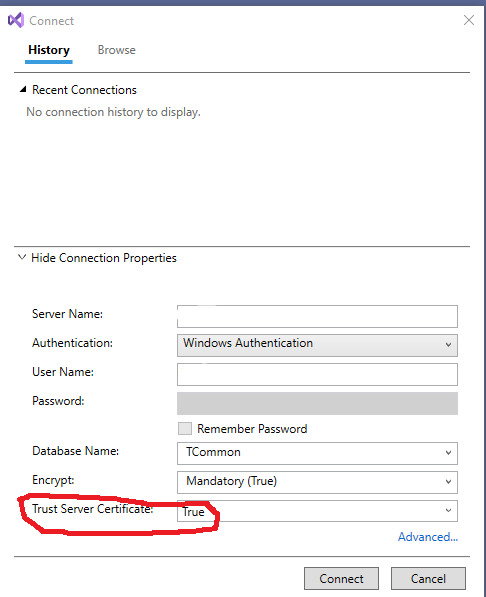
On my workstation, I have to Show Connection Properties, then change the default for Trust Server Certificate to True for it to make a connection. I'm running a test version of SQL Server and didn't set up the certificates.
Click on Connect. Then on the Import Database window, click Start.
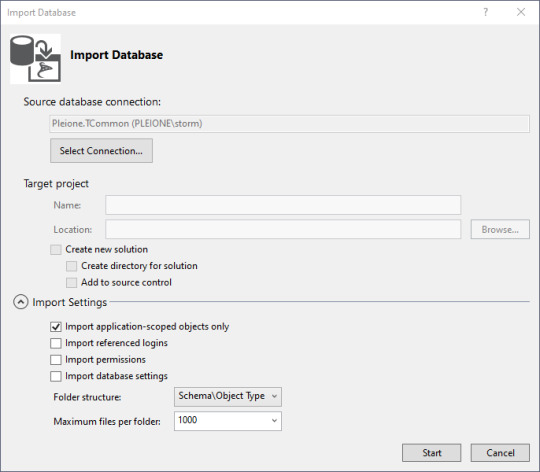
With a blank database, it's fairly anticlimactic, but there really is a connection now to the database, and the properties are copied to your work area. The summary tells you where the log is stored. Then click "Finish" to continue on.
Next, we'll add some objects in. Right click in the Solution Explorer pane, then click Add, then New Item. Lots of little goodies to play with. Since I've been trying to match a project from another site, I need to create a schema to store the objects in. Schemas are part of Security, and there's my little object. I select the schema, give it a name down below, and click Add.
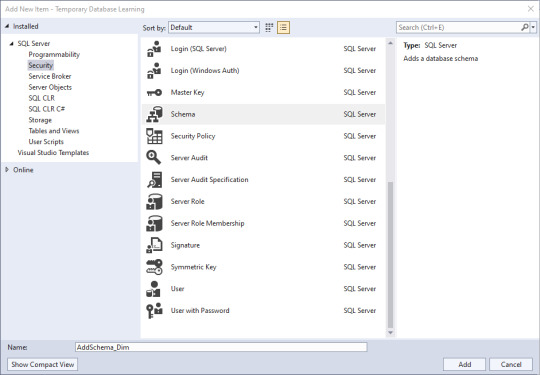
Well, not quite what I expected to happen: CREATE SCHEMA [AddSchema_Dim]
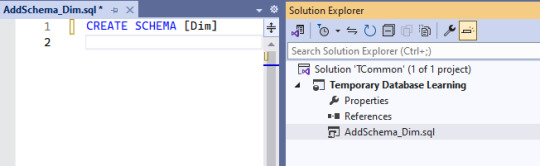
But that's changeable. And in making that change, the solution's object has the name I wanted, and the code has the actual name of the schema I want.
Now, lets add a table.
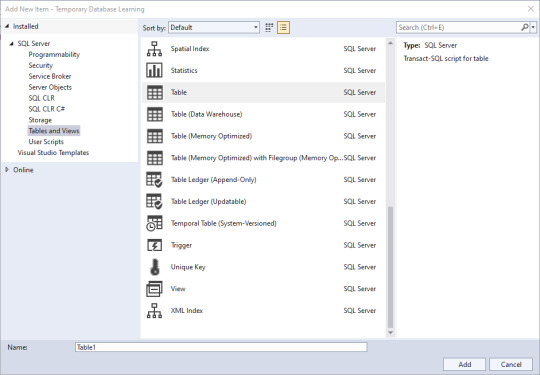
If you're like me, you've used a few of these, but not all of them. Time to do research if you're unsure, but I'm going to go with a simple table for this demonstration. Since I know the name of the solution object will take the name I put in the bottom, I'll name this one AddTable_Dim.Date, and know that I need to edit the actual code.
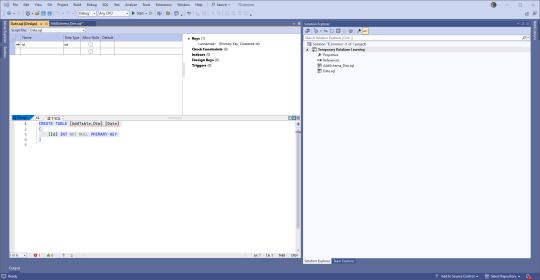
You have choices. If you're used to creating tables using the upper part of the pane where there is a GUI type of set up, go for that. If you're used to typing things out, go to the lower part. Or mix and match! VS will keep the two in sync.
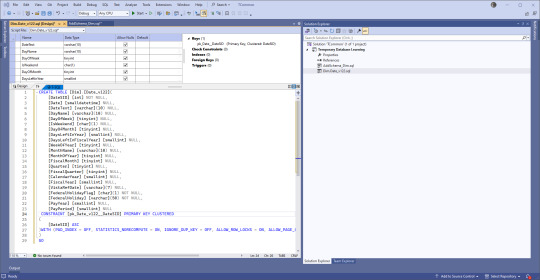
Instead of 'ID' we use 'SID' for Surrogate Identifier. The intake process sets up the unique (across a table) SID values and follows rules that help us track issues backwards to the original location where the data came from.
Second, there's a version number in there. We have the same tables across various enclaves (groups of servers), and we keep the versions the same between all but our development enclave. But instead of forcing our developers and end users to keep up, we use views that are in the databases they work from to expose the data. Many times we don't need to change the views at all which is easier on people that don't need to memorize a few hundred tables and variations.
I'm going to cut this off here, and start working on the next post. Back soon!
0 notes
Text
Using CAST and CONVERT Functions in T-SQL
Using CAST and CONVERT in T-SQL: A Complete Guide for SQL Developers Hello, SQL enthusiasts! In this blog post, I will introduce you to T-SQL CAST and CONVERT Functions – an essential concept in T-SQL: using the CAST and CONVERT functions. These functions help you convert data from one type to another, ensuring compatibility and accuracy in your SQL queries. Understanding when to use CAST and…
0 notes
Text
10+ Ethical Hacking Tools 2024 – Beginner friendly explanation
What are ethical hacking tools?
Ethical hacking tools are digital utilities engineered to assist cybersecurity professionals in conducting authorized tests on computer systems and networks. These tools serve as essential instruments in identifying and rectifying potential security vulnerabilities, helping organizations fortify their digital defenses against malicious cyber threats. Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, leverage these specialized tools to simulate various attack scenarios, mimicking the tactics and techniques employed by real-world cyber adversaries. By utilizing ethical hacking tools, security experts can proactively identify weaknesses in a system's defenses and implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data and assets from potential breaches.
Types of ethical hacking tools?
1. Vulnerability Scanners: Tools like Nessus automate scanning systems and applications for known vulnerabilities, employing techniques like web crawling and code analysis.
2. Network Scanners: Nmap maps and probes networks, identifying active devices, open ports, and potential security weaknesses.
3. Web Application Scanners: Burp Suite is a tool specifically designed for web applications, searching for vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and weak password hashing.
4. Password Cracking Tools: John the Ripper attempts to crack password hashes using techniques like brute-force, dictionary attacks, and rainbow tables.
5. Packet Sniffers: Wireshark captures network traffic for analysis of communication protocols, data exchange, and potential security issues.
6. Social Engineering Tools: The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) simulates phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics to test user awareness and susceptibility to manipulation.
7. Exploitation Frameworks: Metasploit provides a platform for deploying pre-built exploits against identified vulnerabilities.
8. Wireless Security Tools: Aircrack-ng audits the security of wireless networks, uncovering weaknesses in encryption, identifying rogue access points, and cracking weak Wi-Fi passwords.
9. Fuzzers: AFL (American Fuzzy Lop) generates random or mutated data inputs to applications and systems to identify vulnerabilities and improve software robustness.
10. Forensics Tools: Autopsy aids in digital forensics investigations, collecting and analyzing digital evidence from compromised systems.
1.INVICTI
Invicti is a powerful tool for keeping your websites and web applications safe from cyber threats. It's like having an automated security guard that checks your online platforms for any weaknesses that hackers could exploit. What's great is that it works with all kinds of web applications, no matter how they're built.
One unique feature of Invicti is that it doesn't just find security flaws; it also tests them out safely to make sure they're real. For instance, if it finds a vulnerability like SQL injection, it'll even show you proof by revealing the database name. This saves you time and effort since you don't have to double-check everything yourself.
Plus, Invicti makes it easy to understand what needs fixing. If it's not completely sure about a vulnerability, it'll label it as '[Possible]' and give it a certainty rating, so you know which issues are urgent. With Invicti on your side, securing your web applications is a breeze, letting you focus on staying one step ahead of cyber threats
2.THREATMAPPER
Imagine ThreatMapper as your personal superhero for keeping your online stuff safe. It's like a special tool that looks out for bad guys trying to sneak into your cloud-based apps and websites. With ThreatMapper, you can easily check for things like bugs, viruses, and settings that might make it easy for hackers to get in. It's really smart too—it figures out which problems are the most urgent so you can fix them first. Plus, it doesn't matter what kind of cloud system you're using or how your stuff is set up; ThreatMapper can handle it all! Whether you're using regular servers, fancy containers, or even the latest tech like Kubernetes, ThreatMapper has your back.
3.Nmap 7.90
Nmap just got a shiny new update called Nmap 7.90! Nmap, short for "Network Mapper," is like a super helpful tool that anyone can use for free. It's awesome because it helps you find all the devices connected to a network and keeps an eye on their security. People who manage computer networks love using Nmap because it's not only great for figuring out what's connected to their network, but also for planning updates and making sure everything stays up and running smoothly. Plus, it's perfect for keeping an eye on when services go down or if any new devices pop up unexpectedly.
4.Angry IP Scanner 3.9.4
Angry IP Scanner, also known as ipscan! It's like a super-fast detective tool for your computer that helps you explore networks and find out what's connected to them. Whether you're a tech whiz or just someone who's curious, Angry IP Scanner is perfect because it's free, easy to use, and works on any type of computer. It's not just for pros either; lots of people, from big companies to regular folks, use it to keep their networks safe and sound. So, if you've ever wondered what's hiding on your network, Angry IP Scanner is here to help you find out!
Web Application Hacking:
5. Fortify WebInspect:
WebInspect, a tool that's like a security guard for your web applications! It's designed to check your websites and apps while they're running to find any potential security holes. Plus, it works with Microfocus SSC to manage all the security stuff in one place, making things super easy.
Here's what makes Fortify WebInspect awesome:
• It hunts down vulnerabilities in your web apps and APIs while they're live.
• It keeps up with the latest web tech and has built-in rules to follow important security rules.
• It watches for patterns and uses smart analysis to help you fix any problems.
6. Burp Suite Professional
Burp Suite Professional as your ultimate sidekick in the world of web security testing! With Burp Suite, you can automate boring tests and then dive deep into the nitty-gritty with its expert tools. It's not just about finding basic security flaws; Burp Suite helps you tackle advanced stuff too, like the latest hacker tricks and OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities.
Here's why Burp Suite is your best buddy:
• Save time with smart automation: It does the boring stuff for you so you can focus on what you do best.
• Scan all kinds of modern web apps: Whether it's a fancy JavaScript-heavy site or complex APIs, Burp Suite can handle it.
• Spot hidden issues: It's like having x-ray vision for web vulnerabilities, finding stuff others might miss.
• Stay ahead of the curve: With regular updates and cutting-edge research, you'll always be one step ahead.
• Be super productive: It's packed with features to make your testing life easier, from recording your actions to powerful search tools.
• Share your findings easily: Make fancy reports that anyone can understand and appreciate.
• Customize it your way: Whether you want to tweak settings or create your own tools, Burp Suite lets you do it all.
So, if you're serious about web security and want to level up your testing game, Burp Suite Professional is the way to go. But if you're just starting out and want to learn the basics, the Community Edition is perfect for you. Either way, Burp Suite has your back!
7. Grendel-Scan v4
Grendel-Scan, a cool tool for keeping your web apps safe! It's like having a friendly robot that helps you check your websites for sneaky security problems. Grendel-Scan can find common issues all on its own, but it's also great for when you want to do some hands-on testing yourself. If you want to give it a try or learn more, just head over to the Grendel-Scan homepage! It's easy to use and totally free.
8. Cain & Abel v7
Cain and Abel, a handy tool for helping you out if you ever forget your passwords on Windows! Think of it like a friendly wizard that can magically find your passwords using clever tricks. Whether it's through listening to network traffic or trying different combinations, Cain and Abel can work its magic to get your passwords back. So, if you're ever locked out of your account, Cain and Abel might just save the day!
9. Wireshark 4.1.2
a super handy tool for peeking into your network traffic! Imagine it like a detective, quietly watching all the data that travels between your devices and the internet. It can sniff out information from all sorts of connections, like your Wi-Fi or even Bluetooth! Wireshark keeps track of all this data so you can look at it later and see what's going on. It's like having a secret window into your network's world. And guess what? Wireshark is the go-to choice for people all around the globe who need to peek into their network traffic. So, if you ever wonder what's going on behind the scenes of your internet connection, Wireshark is your friend!
10. Maltego 4.4
a super cool tool that turns raw information into useful insights! Think of it as a powerful detective kit for the internet. With Maltego, you can track down people or businesses, figure out who's connected to who, and even find hidden connections between companies and individuals. It's like putting together puzzle pieces to see the bigger picture!
Maltego makes it easy to gather data from different sources, like social media profiles or comments, and organize it into a neat graph. This helps us quickly spot patterns and connections. For example, in just a few minutes, we can use Maltego to track down individuals associated with suspicious activity in our local area by looking at different names they might use.
So, whether you're investigating something or just curious about the web's secrets, Maltego is your trusty sidekick!
11.John the Ripper Jumbo v1.9.0
John the Ripper, the speedy password detective! Its main job? Finding those weak passwords hiding on Unix systems. But it doesn't stop there—it's also great at cracking Windows passwords and many other types of codes.
Here's how it works: John the Ripper is like a secret agent that automatically figures out how a password is encrypted. Then, it checks it against a huge list of common passwords. When it finds a match, it's like solving a puzzle!
Are you a beginner or do you already have experience in the IT sector? Not sure where to start? Join Blitz Academy and enroll in our Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH) course from industry experts. At Blitz Academy, located in Kerala, we offer top-notch cyber security and ethical hacking courses in Kerala and throughout the region. Learn from the No.1 institute in Kerala and gain valuable skills in cyber security and ethical hacking. With our comprehensive courses, you'll be equipped to tackle the challenges of today's digital world with confidence. Sign up now and take the first step towards a successful career in cyber security!
0 notes
Text
What is Full Stack Development

Full stack development refers to the practice of working on both the front end and back end parts of a web application. A full stack developer is proficient in multiple programming languages and frameworks, allowing them to handle all aspects of the development process.
The front end of a web application is what users interact with directly. It includes the user interface, design elements, and functionalities visible to users in their browsers. Front end technologies commonly used by full stack developers include HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, along with frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js for building interactive user interfaces.
On the other hand, the back end of a web application deals with server-side operations, database management, and business logic. Full stack developers work with back end technologies such as programming languages like Python, Ruby, Java, or JavaScript (Node.js), along with frameworks like Express.js, Django, Flask, or Spring Boot for handling server-side logic and data management.
In addition to front end and back end development, full stack developers are often familiar with databases (SQL or NoSQL) for storing and retrieving data, as well as version control systems like Git for managing code changes. They may also have knowledge of deployment processes and cloud platforms for hosting web applications.
Being proficient in both front end and back end technologies allows full stack developers to create complete, end-to-end solutions for web development projects. They can work on all layers of an application, from designing user interfaces to implementing server-side logic and deploying the final product, making them versatile and valuable assets to development teams.
Full Stack Development Roadmap

Sure, here's a comprehensive roadmap for full-stack development:
Basic Programming Skills
Learn a programming language like Python, JavaScript, or Java.
Understand concepts like variables, data types, control structures, and functions.
Version Control Systems
Familiarize yourself with Git and GitHub for version control and collaboration.
Front-End Development
HTML: Learn to create the structure of web pages.
CSS: Style your web pages and make them visually appealing.
JavaScript: Understand client-side scripting for interactive elements and dynamic content.
Front-End Frameworks and Libraries
Learn popular libraries/frameworks like React, Angular, or Vue.js for efficient front-end development.
Responsive Design and CSS Frameworks
Master responsive design principles using CSS frameworks like Bootstrap or Tailwind CSS.
Back-End Development
Choose a back-end language/framework such as Node.js, Python (Django, Flask), Ruby (Ruby on Rails), or Java (Spring Boot).
Learn about databases (SQL and NoSQL) and how to interact with them.
RESTful APIs
Understand how to design and consume RESTful APIs for communication between front-end and back-end.
Database Management
Learn SQL for relational databases like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or SQL Server.
Explore NoSQL databases like MongoDB or Firebase for non-relational data storage.
Authentication and Authorization
Implement user authentication and authorization using frameworks like OAuth, JWT, or sessions.
Testing and Debugging
Learn testing frameworks like Jest, Mocha, or Selenium for automated testing.
Practice debugging techniques to troubleshoot and fix issues in your applications.
Deployment and DevOps
Understand deployment strategies using platforms like AWS, Heroku, or DigitalOcean.
Learn about containers (Docker) and container orchestration (Kubernetes) for scalable deployments.
Familiarize yourself with continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines.
Security
Learn about common security vulnerabilities and how to mitigate them (e.g., OWASP Top 10).
Implement security best practices such as input validation, secure authentication, and HTTPS.
Performance Optimization
Optimize your applications for speed and performance using techniques like caching, lazy loading, and code splitting.
Continuous Learning and Improvement
Stay updated with new technologies, frameworks, and best practices in full-stack development.
Participate in online communities, attend webinars/conferences, and collaborate on open-source projects.
Soft Skills
Develop communication skills for effective collaboration with team members and stakeholders.
Practice problem-solving and critical thinking to tackle complex development challenges.
By following this roadmap and continuously honing your skills, you'll become a proficient full-stack developer capable of building robust and scalable web applications.
Java Full Stack Roadmap

Sure, here's a roadmap for becoming a Java Full Stack developer:
Learn Core Java
Start by learning the basics of Java programming language including syntax, data types, control flow, object-oriented programming concepts (classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism), exception handling, and input/output operations.
Understand Data Structures and Algorithms
Gain a solid understanding of fundamental data structures like arrays, linked lists, stacks, queues, trees, and graphs. Also, learn algorithms for searching, sorting, and basic computational problems.
Learn Relational Databases
Study SQL (Structured Query Language) and relational database concepts. Learn how to design and interact with databases using tools like MySQL, PostgreSQL, or Oracle.
Web Development Basics
Learn HTML, CSS, and JavaScript for front-end development. Understand how to create static web pages, style them, and add interactivity using JavaScript.
Backend Development with Java
Dive into server-side development with java full stack roadmap . Learn about Servlets, JavaServer Pages (JSP), and Java frameworks like Spring Boot for building robust and scalable web applications.
Database Connectivity
Understand JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) for connecting Java applications with relational databases. Learn how to perform CRUD operations (Create, Read, Update, Delete) using JDBC.
Frontend Frameworks
Explore modern front-end frameworks like React.js, Angular, or Vue.js to build dynamic and interactive user interfaces for your Java web applications.
RESTful Web Services
Learn about REST (Representational State Transfer) architecture and develop RESTful web services using Java frameworks like Spring Boot or JAX-RS.
Version Control Systems
Familiarize yourself with version control systems like Git for managing your codebase, collaborating with teams, and tracking changes effectively.
Testing and Quality Assurance
Learn about software testing methodologies, unit testing frameworks like JUnit, and integration testing for ensuring the quality and reliability of your Java applications.
Containerization and Deployment
Understand containerization concepts using Docker for packaging and deploying your Java applications. Learn about container orchestration tools like Kubernetes for managing containers at scale.
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
Explore CI/CD pipelines using tools like Jenkins, GitLab CI/CD, or Travis CI to automate the build, test, and deployment processes of your Java applications.
Cloud Platforms
Familiarize yourself with cloud platforms like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for hosting, scaling, and managing your Java applications in the cloud environment.
Security Practices
Learn about web application security best practices, including authentication, authorization, data encryption, and protection against common security threats like SQL injection, XSS, CSRF, etc.
Continuous Learning and Growth
Stay updated with the latest trends, tools, and technologies in the Java ecosystem. Engage in continuous learning through online courses, workshops, conferences, and community forums.
By following this roadmap and continuously honing your skills, you can become a proficient Java Full Stack developer capable of designing, developing, and deploying end-to-end web applications.
Python Full Stack Syllabus

Sure, here's a sample syllabus for a python full stack syllabus. Keep in mind that this is a general outline, and the actual content and duration of each topic may vary based on the course's depth and focus.
Week 1-2: Introduction to Python
Introduction to Python programming language
Variables, data types, and operators
Control structures: loops and conditionals
Functions and modules
Introduction to Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) in Python
Week 3-4: Front-End Development
Introduction to front-end development
HTML5 fundamentals
CSS3 basics: styling and layout
Introduction to JavaScript and DOM manipulation
Responsive web design using media queries
Week 5-6: Back-End Development with Flask
Introduction to back-end development
Introduction to Flask framework
Routing and views in Flask
Templates and Jinja2
Handling forms and form validation
Working with databases using Flask-SQLAlchemy
Week 7-8: Database Management
Introduction to Relational Databases (SQL)
SQL queries: CRUD operations
Database design and normalization
Introduction to ORM (Object-Relational Mapping)
Using SQLAlchemy ORM with Flask for database interactions
Week 9-10: Front-End Frameworks (React or Angular)
Introduction to front-end frameworks (React or Angular)
Setting up a front-end framework project
Components, props, and state management
Routing and navigation
Fetching data from APIs
Week 11-12: Deployment and Project
Introduction to deployment strategies
Deploying Flask applications on platforms like Heroku or AWS
Connecting front-end and back-end applications
Final project: Full-stack web application development using Python, Flask, and a front-end framework
Assessment:
Weekly quizzes and assignments
Mid-term project: Build a CRUD application using Flask and SQLAlchemy
Final project: Full-stack web application development project with deployment
Resources:
Online tutorials and documentation
Recommended textbooks and reading materials
Coding exercises and practice projects
Note: This syllabus is a general guideline and may be adjusted based on the instructor's preferences and the specific learning objectives of the course.
Skills Required for Full Stack Development

Full stack development is a comprehensive approach to web development that involves working on both the front end and back end of a web application. To excel in full stack development, you need a diverse set of skills that encompass various technologies, languages, frameworks, and tools. Here are the key skills required for full stack development:
Front-end Development:
HTML/CSS: Proficiency in creating and styling web pages using HTML for structure and CSS for presentation.
JavaScript (JS): Strong understanding of JS for interactive and dynamic user experiences. Familiarity with modern frameworks/libraries like React, Angular, or Vue.js is beneficial.
Responsive Design: Ability to design websites that adapt and function seamlessly across different devices and screen sizes.
Back-end Development:
Programming Languages: Proficiency in at least one server-side language such as JavaScript (Node.js), Python (Django/Flask), Ruby (Ruby on Rails), Java (Spring Boot), or PHP (Laravel).
Databases: Knowledge of database management systems like MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB, or NoSQL databases for storing and retrieving data efficiently.
API Development: Experience in building RESTful or GraphQL APIs to enable communication between the front end and back end of the application.
Database Management:
Database Design: Understanding of database modeling, normalization, indexing, and optimization techniques.
SQL/NoSQL: Proficiency in writing SQL queries for relational databases and knowledge of NoSQL query languages for non-relational databases.
Server Management and Deployment:
Web Servers: Familiarity with web servers like Apache, Nginx, or Microsoft IIS for hosting web applications.
Cloud Platforms: Experience in deploying applications on cloud platforms such as AWS, Azure, Google Cloud Platform, or Heroku.
Containerization: Knowledge of containerization tools like Docker for creating, deploying, and managing application containers.
Version Control:
Git: Proficiency in using Git for version control, collaboration, and managing code repositories (e.g., GitHub, GitLab, Bitbucket).
DevOps and CI/CD:
Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): Understanding of CI/CD pipelines to automate testing, building, and deployment processes.
DevOps Tools: Familiarity with DevOps tools such as Jenkins, Travis CI, CircleCI, or GitLab CI/CD for automation and infrastructure management.
Software Development Lifecycle (SDLC):
Agile Methodologies: Knowledge of Agile practices like Scrum or Kanban for iterative development, collaboration, and project management.
Additional Skills (optional but beneficial):
Security: Awareness of web security principles, practices, and tools (e.g., HTTPS, OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities).
UI/UX Design: Basic understanding of user interface and user experience design principles for creating intuitive and user-friendly interfaces.
Testing: Familiarity with testing frameworks like Jest, Mocha, Jasmine for unit testing, integration testing, and end-to-end testing.
Career Opportunities in Full Stack Development
Full Stack Developers are in high demand across industries, including IT companies, startups, e-commerce platforms, and more. Job roles may include Full Stack Developer, Web Developer, Software Engineer, and Application Developer. Salaries for Full Stack Developers vary based on experience, location, and company size but generally offer competitive pay and opportunities for career growth.
Conclusion
Full Stack Development offers a rewarding career path for tech enthusiasts looking to work on diverse projects and contribute to innovative solutions in the digital landscape. By mastering the necessary skills and staying updated with industry trends, individuals can embark on a successful journey in Full Stack Development.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
What programming languages are essential for Full Stack Development?
Full Stack Developers often need to be proficient in languages like Java, Python, JavaScript, and frameworks associated with them.
How long does it take to become a Full Stack Developer?
The time required to become a Full Stack Developer varies depending on prior experience, learning pace, and the complexity of technologies being mastered. It can range from several months to a couple of years.
Is Full Stack Development a good career choice?
Yes, Full Stack Development offers excellent career prospects with a high demand for skilled professionals and competitive salaries in the tech industry.
What are the typical responsibilities of a Full Stack Developer?
Full Stack Developers are responsible for designing, developing, testing, and deploying web applications, along with troubleshooting and maintaining existing systems.
How can one stay updated with the latest trends in Full Stack Development?
To stay updated, professionals can join tech communities, attend workshops, enroll in online courses, and regularly follow industry blogs and forums
0 notes
Text
10+ Ethical Hacking Tools 2024 – Beginner friendly explanation
What are ethical hacking tools?
Ethical hacking tools are digital utilities engineered to assist cybersecurity professionals in conducting authorized tests on computer systems and networks. These tools serve as essential instruments in identifying and rectifying potential security vulnerabilities, helping organizations fortify their digital defenses against malicious cyber threats. Ethical hackers, also known as white-hat hackers, leverage these specialized tools to simulate various attack scenarios, mimicking the tactics and techniques employed by real-world cyber adversaries. By utilizing ethical hacking tools, security experts can proactively identify weaknesses in a system's defenses and implement robust security measures to safeguard sensitive data and assets from potential breaches.
Types of ethical hacking tools?
1. Vulnerability Scanners: Tools like Nessus automate scanning systems and applications for known vulnerabilities, employing techniques like web crawling and code analysis.
2. Network Scanners: Nmap maps and probes networks, identifying active devices, open ports, and potential security weaknesses.
3. Web Application Scanners: Burp Suite is a tool specifically designed for web applications, searching for vulnerabilities like SQL injection, cross-site scripting, and weak password hashing.
4. Password Cracking Tools: John the Ripper attempts to crack password hashes using techniques like brute-force, dictionary attacks, and rainbow tables.
5. Packet Sniffers: Wireshark captures network traffic for analysis of communication protocols, data exchange, and potential security issues.
6. Social Engineering Tools: The Social-Engineer Toolkit (SET) simulates phishing attacks and other social engineering tactics to test user awareness and susceptibility to manipulation.
7. Exploitation Frameworks: Metasploit provides a platform for deploying pre-built exploits against identified vulnerabilities.
8. Wireless Security Tools: Aircrack-ng audits the security of wireless networks, uncovering weaknesses in encryption, identifying rogue access points, and cracking weak Wi-Fi passwords.
9. Fuzzers: AFL (American Fuzzy Lop) generates random or mutated data inputs to applications and systems to identify vulnerabilities and improve software robustness.
10. Forensics Tools: Autopsy aids in digital forensics investigations, collecting and analyzing digital evidence from compromised systems.
1.INVICTI
Invicti is a powerful tool for keeping your websites and web applications safe from cyber threats. It's like having an automated security guard that checks your online platforms for any weaknesses that hackers could exploit. What's great is that it works with all kinds of web applications, no matter how they're built.
One unique feature of Invicti is that it doesn't just find security flaws; it also tests them out safely to make sure they're real. For instance, if it finds a vulnerability like SQL injection, it'll even show you proof by revealing the database name. This saves you time and effort since you don't have to double-check everything yourself.
Plus, Invicti makes it easy to understand what needs fixing. If it's not completely sure about a vulnerability, it'll label it as '[Possible]' and give it a certainty rating, so you know which issues are urgent. With Invicti on your side, securing your web applications is a breeze, letting you focus on staying one step ahead of cyber threats
2.THREATMAPPER
Imagine ThreatMapper as your personal superhero for keeping your online stuff safe. It's like a special tool that looks out for bad guys trying to sneak into your cloud-based apps and websites. With ThreatMapper, you can easily check for things like bugs, viruses, and settings that might make it easy for hackers to get in. It's really smart too—it figures out which problems are the most urgent so you can fix them first. Plus, it doesn't matter what kind of cloud system you're using or how your stuff is set up; ThreatMapper can handle it all! Whether you're using regular servers, fancy containers, or even the latest tech like Kubernetes, ThreatMapper has your back.
3.Nmap 7.90
Nmap just got a shiny new update called Nmap 7.90! Nmap, short for "Network Mapper," is like a super helpful tool that anyone can use for free. It's awesome because it helps you find all the devices connected to a network and keeps an eye on their security. People who manage computer networks love using Nmap because it's not only great for figuring out what's connected to their network, but also for planning updates and making sure everything stays up and running smoothly. Plus, it's perfect for keeping an eye on when services go down or if any new devices pop up unexpectedly.
4.Angry IP Scanner 3.9.4
Angry IP Scanner, also known as ipscan! It's like a super-fast detective tool for your computer that helps you explore networks and find out what's connected to them. Whether you're a tech whiz or just someone who's curious, Angry IP Scanner is perfect because it's free, easy to use, and works on any type of computer. It's not just for pros either; lots of people, from big companies to regular folks, use it to keep their networks safe and sound. So, if you've ever wondered what's hiding on your network, Angry IP Scanner is here to help you find out!
Web Application Hacking:
5. Fortify WebInspect:
WebInspect, a tool that's like a security guard for your web applications! It's designed to check your websites and apps while they're running to find any potential security holes. Plus, it works with Microfocus SSC to manage all the security stuff in one place, making things super easy.
Here's what makes Fortify WebInspect awesome:
• It hunts down vulnerabilities in your web apps and APIs while they're live.
• It keeps up with the latest web tech and has built-in rules to follow important security rules.
• It watches for patterns and uses smart analysis to help you fix any problems.
0 notes
Text
8 Engaging Games for Developing Programming Skills

1. Oh My Git!
Git, an essential tool for software developers, can be daunting for beginners. _Oh My Git!_ addresses this challenge by providing a gamified introduction to Git commands and file manipulation. With visualizations of Git commands, this game allows developers to understand the effects of their instructions on files. Players can progress through levels to learn increasingly complex Git techniques, test commands on real Git repositories within the game, and practice remote interactions with team members.
Cost: Free
2. Vim Adventures
Vim, a powerful code editor, is a valuable skill for developers, but its command-line interface can be intimidating for beginners. _Vim Adventures_ offers an innovative approach to teaching essential Vim commands through gameplay. Players navigate through the game and solve puzzles using commands and keyboard shortcuts, effectively making these commands feel like second nature. This game provides a fun experience that eases the learning curve of Vim usage.
Cost: Free demo level; $25 for six months access to the full version.
3. CSS Diner
Styling front-end applications with CSS can be challenging due to the intricate rules of CSS selection. _CSS Diner_ aims to teach developers these rules through a game that uses animated food arrangements to represent HTML elements. Players are prompted to select specific food items by writing the correct CSS code, offering an interactive and engaging way to understand CSS selection.
Cost: Free
4. Screeps
_Screeps_ combines JavaScript programming with massively multiplayer online gameplay, creating self-sustaining colonies. Geared towards developers comfortable with JavaScript, this game allows players to interact through an interface similar to browser developer tools, enabling them to write and execute JavaScript code. The game also facilitates interactions between players, such as trading resources and attacking each other's colonies.
Cost: $14.99 on Steam
5. SQL Murder Mystery
Combining SQL queries with real sleuthing, _SQL Murder Mystery_ challenges players to execute SQL queries to gather information about a murder and find the culprit. This game effectively teaches different ways of extracting data and metadata using SQL queries, making it an entertaining and educational experience for novice and experienced players.
Cost: Free
6. Shenzhen I/O
In _Shenzhen I/O_, players take on the role of an engineer tasked with designing computer chips at a fictional electronics company. The game provides challenges that help players visualize the interface between hardware and software, emphasizing the efficient design of circuits. With a 47-page employee reference manual as the only source of help, players are expected to read the manual for instructions, making the game both educational and engaging.
Cost: $14.99 on Steam
7. Human Resource Machine
In _Human Resource Machine_, players work at a corporation where employees are automated instead of the work itself. Players program employee minions doing assembly-line work, using draggable commands that mimic assembly language. The game's design, combined with a grimly whimsical narrative, offers an entertaining way to understand programming concepts.
Cost: $14.99 on Steam
8. While True: learn()
_Machine learning can feel complex to those not familiar with it, but_ while True: learn() _aims to demystify it. The game takes players through different types of machine learning techniques, introducing new techniques in the order that they were invented in the real world. This game offers an engaging way to understand the steps involved in building working machine learning models.
Cost: $12.99 on Steam
These games provide an engaging and interactive approach to learning and practicing programming skills. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, incorporating these games into your learning journey can enhance your understanding of programming concepts and technologies in a fun way.
Level up your programming skills while having a great time!
#gaming#skills#tutortacademy#tutort#learning#excel#technical#education#programming languages#programming#programmingskills
0 notes